
The Coffee Plant's
Best Kept Secret
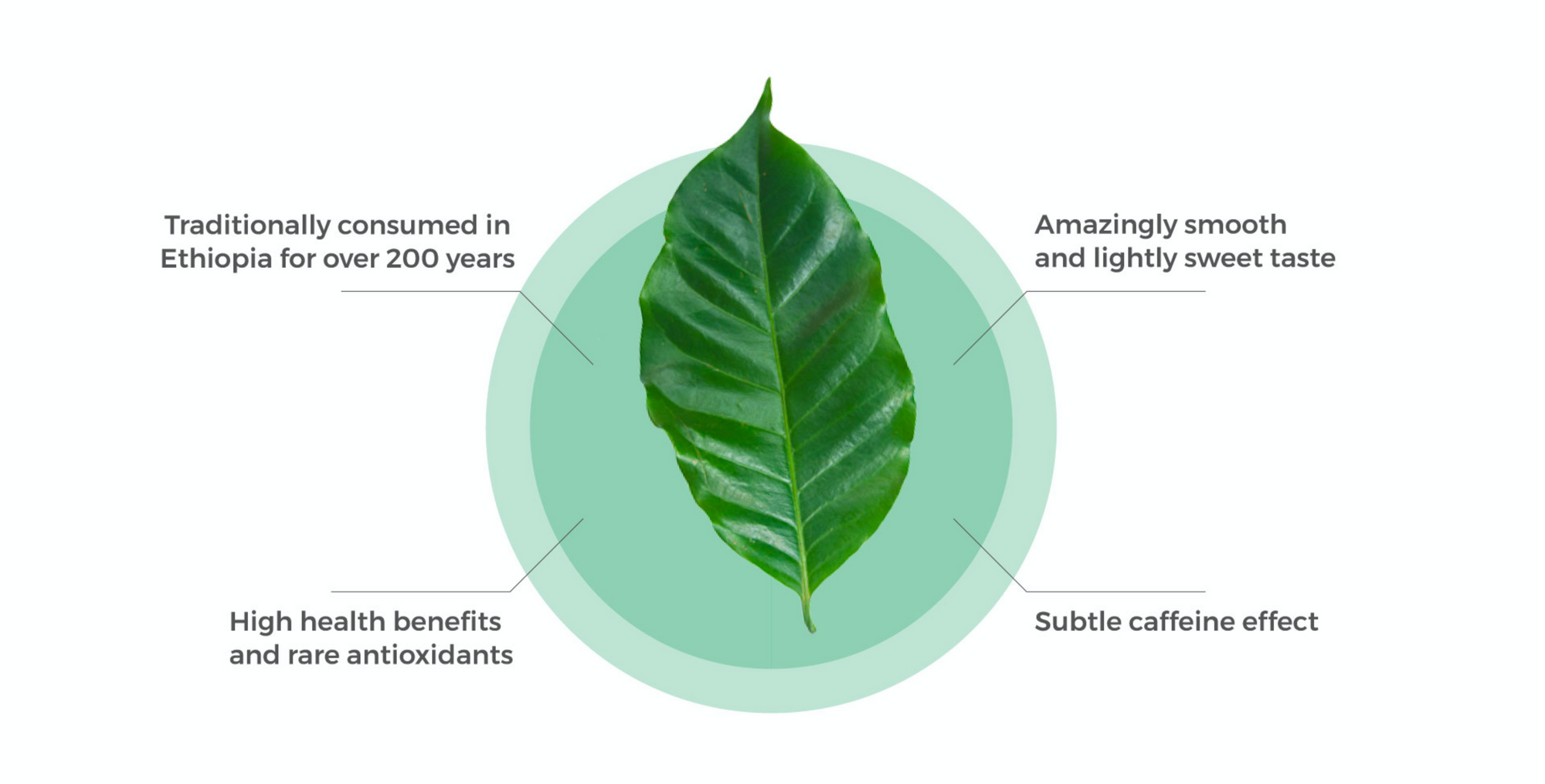

Years of Tradition
Coffee Leaf Tea has been traditionally consumed for hundreds of years in Ethiopia and Indonesia for various reasons like “helping clear the cobwebs,” “stem hunger,” and as a strong anti-inflammatory agent. We reinvented it with modern tea techniques to enhance its taste and unlock its true health potential.
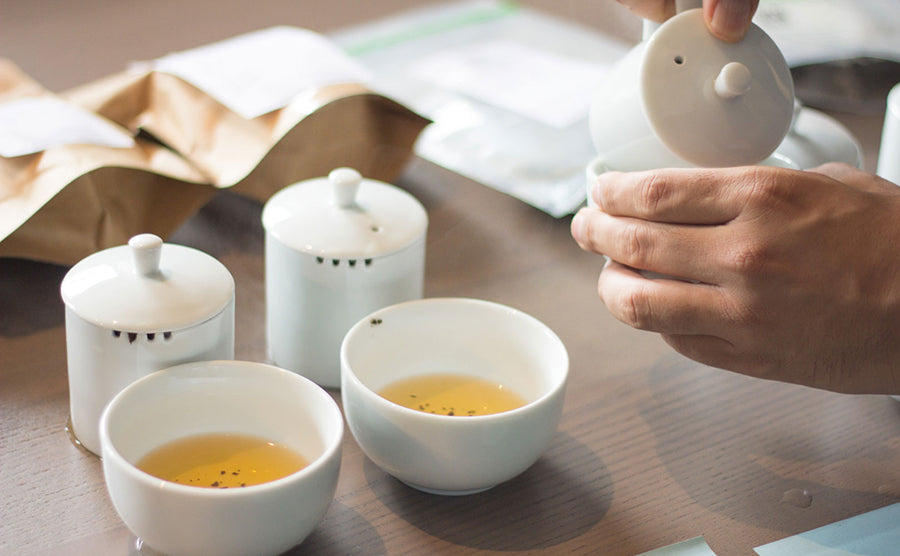


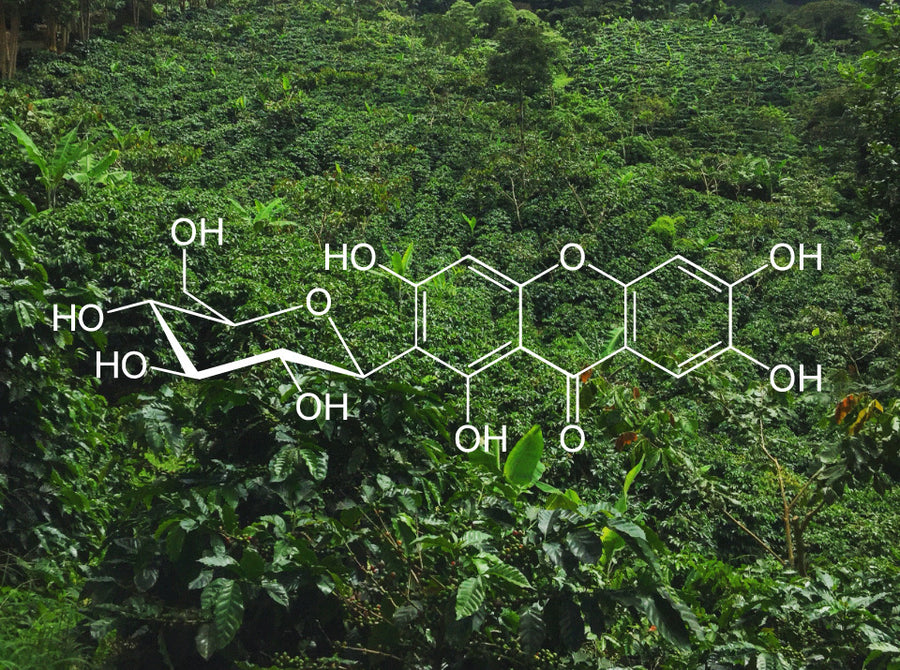

Mangiferin
This unique polyphenol is traditionally found in mangoes and used in ethno-medicine around the world. It has been extensively studied in the recent years for its strong antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, with potential to lower blood sugar and reduce high blood pressure.
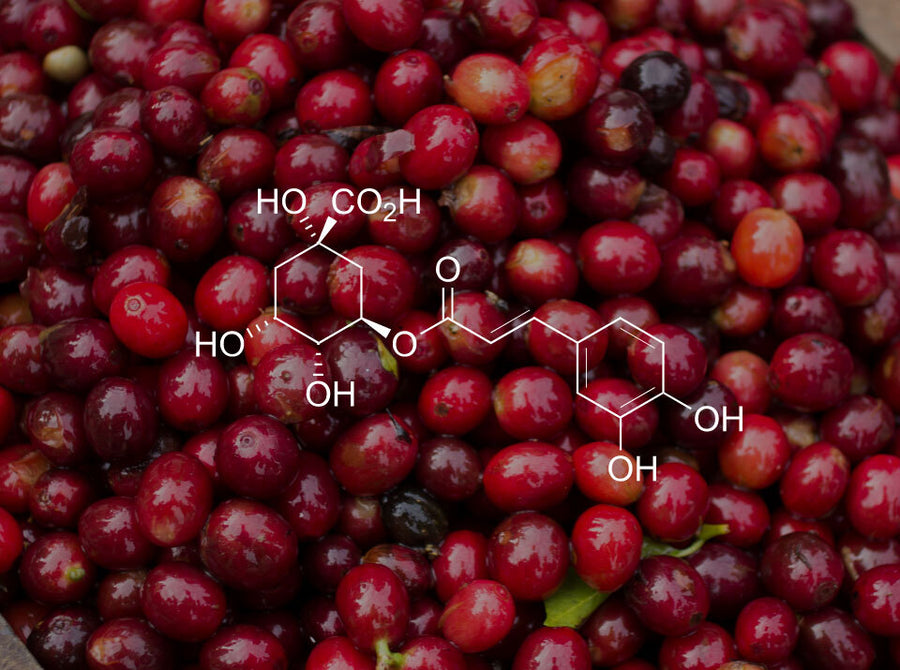
LEARN MORE Chlorogenic Acids
Also found in green coffee beans, they have made green coffee extract wildly popular in health and nutrition circles due to their antioxidant and metabolism-boosting effects.
LEARN MORE
SOURCE:
Chlorogenic Acids
EGCG
Catechins have been popularized by green tea, and are known for their potential to reduce inflammation, aid weight loss, and help prevent heart and brain disease.
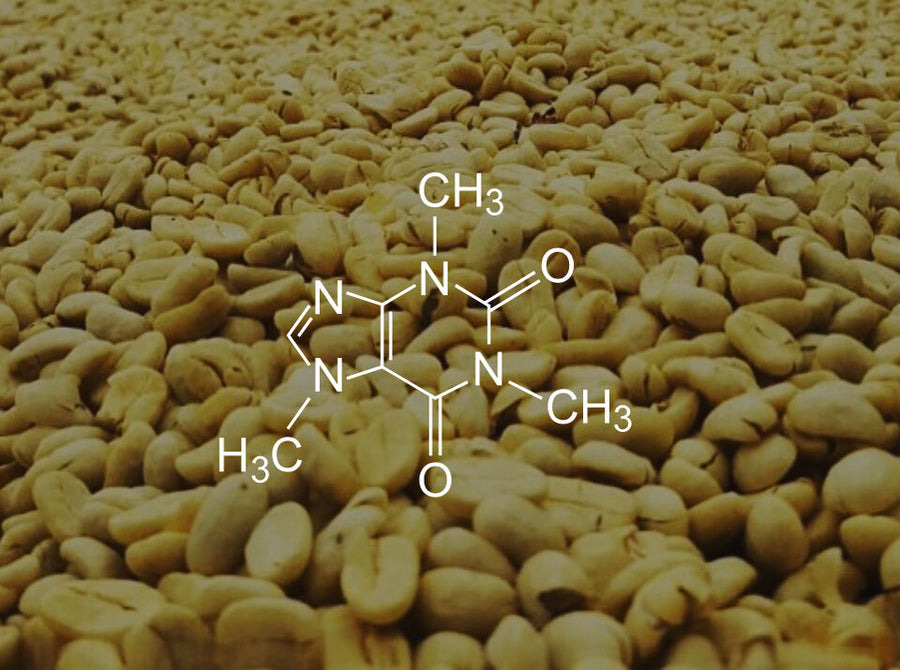
LEARN MORE Theobromine
This alkaloid also found in cacao is a known stimulant but is unlikely to keep you awake at night. It also has been linked to helping reduce risk of heart diseases and improved cognitive functions.
LEARN MORE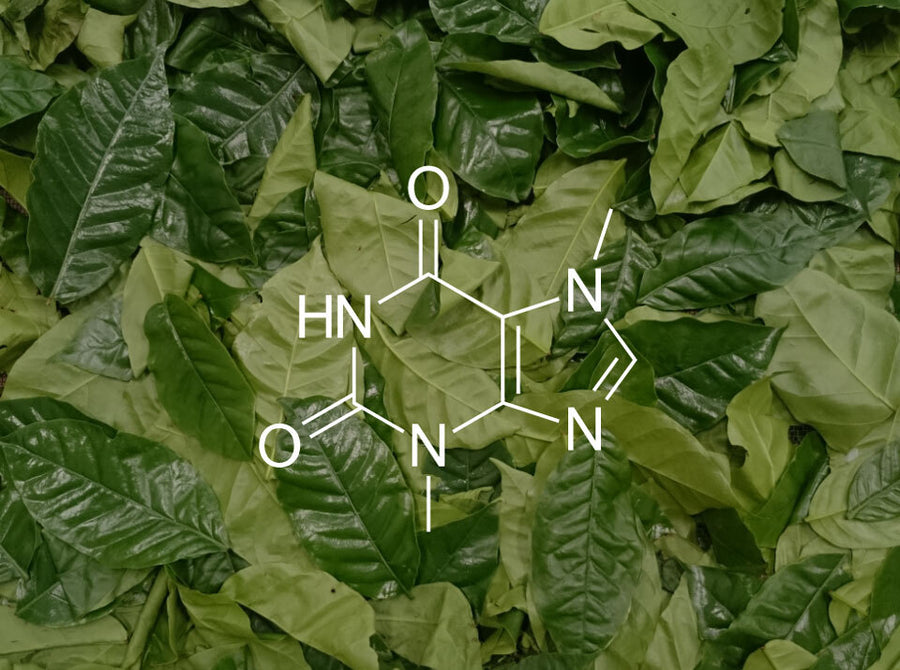 
Research Hub
It is believed that coffee leaves...
- Mangiferin: a natural miracle bioactive compound against lifestyle related disorders
- Characterization of phytochemical mixtures with inflammatory modulation potential from coffee leaves processed by green and black tea processing methods
- Effects of processing method and age of leaves on phytochemical profiles and bioactivity of coffee leaves
- Free radical scavenging activities of phytochemical mixtures and aqueous methanolic extracts recovered from processed coffee leaves
- A combined experimental–theoretical study of the acid–base behavior of mangiferin: implications for its antioxidant activity
- Effects of mangiferin on MAPK signaling pathway in chronic inflammation
- In vitro and in vivo antioxidant properties of chlorogenic acid and caffeic acid
- Chlorogenic acid prevents inflammatory responses in IL‑1β‑stimulated human SW‑1353 chondrocytes, a model for osteoarthritis
- Effect of mangiferin on hyperglycemia and atherogenicity in STZ diabetic rats
- Identification of mangiferin as a potential Glucokinase activator by structure-based virtual ligand screening
- Mangiferin induces islet regeneration in aged mice through regulating p16INK4a
- Protective nature of mangiferin on oxidative stress and antioxidant status in tissues of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats
- Mangiferin attenuates osteoclastogenesis, bone resorption, and RANKL-induced activation of NF-κB and ERK
- Mangiferin: a natural miracle bioactive compound against lifestyle related disorders
- Mangiferin: Possible uses in the prevention and treatment of mixed osteoarthritic pain
- Mangiferin enhances endochondral ossification‐based bone repair in massive bone defect by inducing autophagy through activating AMP‐activated protein kinase signaling pathway
- Mangiferin positively regulates osteoblast differentiation and suppresses osteoclast differentiation
- Mangiferin and Cancer: Mechanisms of Action
- The inhibitory effects of mangiferin, a naturally occurring glucosylxanthone, in bowel carcinogenesis of male F344 rats
- The potential role of mangiferin in cancer treatment through its immunomodulatory, anti-angiogenic, apoptopic, and gene regulatory effects
- Mangiferin: a promising anticancer bioactive
- Mangiferin is not only a remarkable anti-inflammatory compound but also an antitumor agent.
- Anti-angiogenic effects of mangiferin and mechanism of action in metastatic melanoma
- Mangiferin functionalized radioactive gold nanoparticles (MGF-198AuNPs) in prostate tumor therapy: green nanotechnology for production, in vivo tumor retention and evaluation of therapeutic efficacy
- Roles of chlorogenic Acid on regulating glucose and lipids metabolism: a review
- Mangiferin protect myocardial insults through modulation of MAPK/TGF-β pathways
- The Effect of Mangiferin on Improving Endothelial Dysfunction by Inhibiting Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress to Alleviate Mitochondrial Fission
- Cardioprotective effect of mangiferin on isoproterenol induced myocardial infarction in rats
- The Effects of Mangiferin (Mangifera indica L) in Doxorubicin-induced Cardiotoxicity in Ratsink
- Mangiferin Attenuates Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via MAPK/Nrf-2/HO-1/NF-κB In Vitro and In Vivo
- Mangiferin suppressed advanced glycation end products (AGEs) through NF-κB deactivation and displayed anti-inflammatory effects in streptozotocin and high fat diet-diabetic cardiomyopathy rats
- Mangiferin supplementation improves serum lipid profiles in overweight patients with hyperlipidemia: a double-blind randomized controlled trial
- Mangiferin Stimulates Carbohydrate Oxidation and Protects Against Metabolic Disorders Induced by High-Fat Diets
- Mangiferin Decreases Plasma Free Fatty Acids through Promoting Its Catabolism in Liver by Activation of AMPK
- Mangiferin induces the expression of a thermogenic signature via AMPK signaling during brown-adipocyte differentiation
- Evaluation of Antiobesity Effect of Mangiferin in Adipogenesis‐Induced Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells by Assessing Adipogenic Genes
- Beneficial effects of mangiferin on hyperlipidemia in high-fat-fed hamsters



























